The ubiquitous availability of high-speed internet and increasing smartphone ownership are at the forefront of the new era of digital transformation. The entire mobile ecosystem is experiencing significant growth and
The ubiquitous availability of high-speed internet and increasing smartphone ownership are at the forefront of the new era of digital transformation. The entire mobile ecosystem is experiencing significant growth and
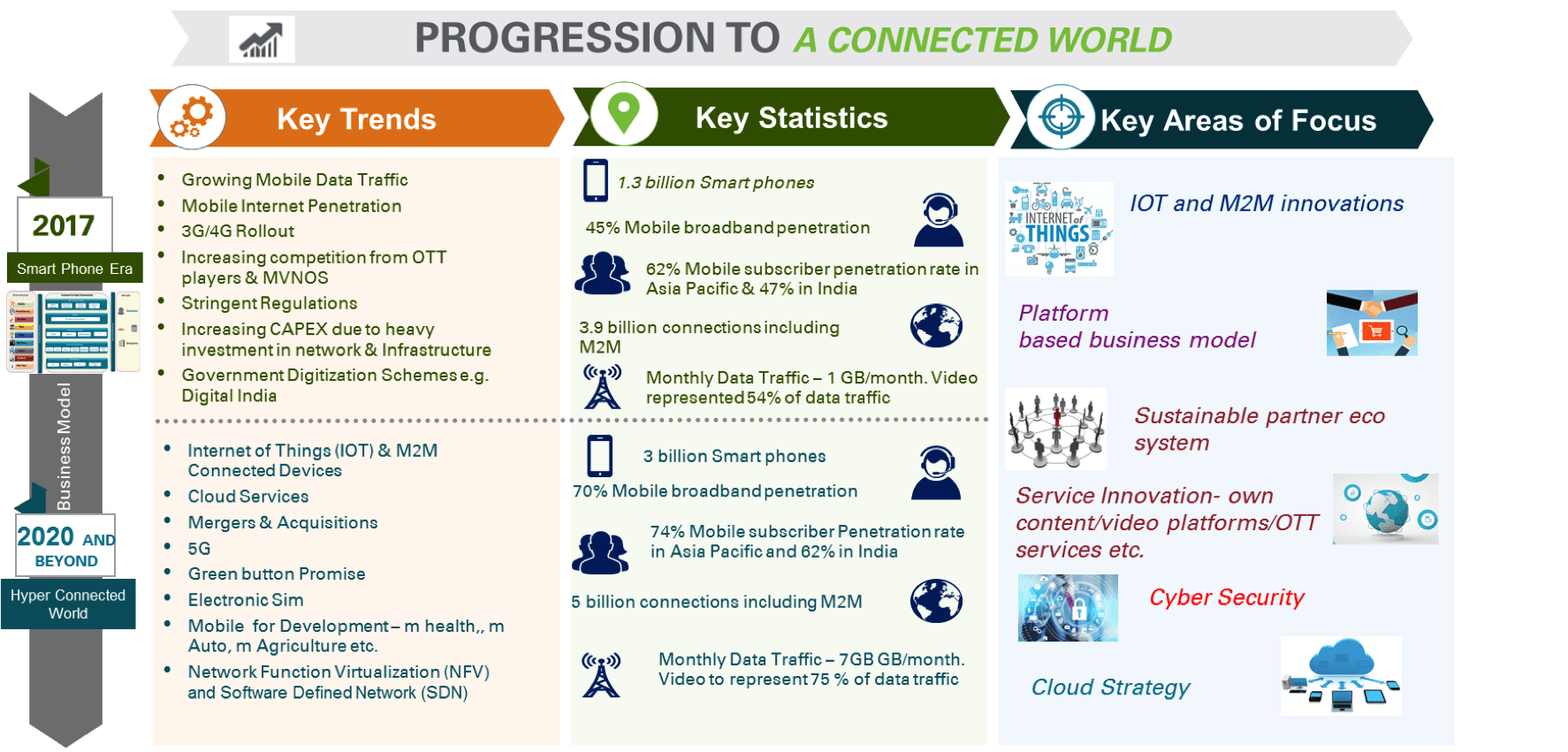
- There will be 8 billion smartphones users by 2020 as compared to the 2.6 billion at the end of 2015
- Data Traffic will grow by a CAGR of 49% by 2020
- Mobile Internet penetration to reach 60 % by 2020 from 44% in 2015
However, despite the growth in the overall mobile ecosystem, Communications Service Providers (CSPs) across the world are facing saturated markets, experiencing slow subscriber growth and stagnated revenue as their core services are being increasingly commoditized by new internet giants & OTT players.
Operators are constantly striving to keep up with the rapidly changing preferences of customers who rely more on recommendations from friends, colleagues, acquaintances and online customer opinions across various social media sites than normal corporate marketing messages. This requires a paradigm shift in how CSPs engage with their customers. We can illustrate the evolutionary journey of the telecommunication industry from a “Smartphone era” to a “Hyper-Connected World” in the following figure. The new business models of individual telcos will be the key enablers in this path-breaking journey.
As the CSPs move from being the a conventional service provider to being the Digital Service Providers (DSPs) who provide the functional platform that enables the customers to go to the market (e.g. using self-service mobile payment apps to pay utility bills generated by Smart meter), they need to move towards a sustainable business model. It will also be imperative for them to prioritise business requirements in order to identify the key use cases which will reap significant benefits while at the same time being relatively easier to implement.
The following are some of the use cases which can leverage the enormous amounts of unstructured text data from social media, call centre data, browsing histories, log files, network analyser, etc. to derive actionable insights
- Real Time Congestion and Customer Offload Management
- Real-Time Personalised offers based on browsing history, device, location, live interactions
- Product/service innovation e.g. payment banks, mobile money etc. and Product/Service Pricing
- Preventive action on network failure
- CAPEX/OPEX optimisation through the use of Network Function Virtualization (NFV) and Software-defined Networking (SDN)
- Call centre, Workforce, and Inventory Optimisation
Thus, moving forward, operators need to move towards a disruptive business model and chalk out a business strategy for an enterprise-wide digital transformation with focus on the following key areas
- Digital Customer Journey Map which succinctly portrays the rapidly changing expectations and experiences of customers across multiple channels/touchpoints
- Enterprise-wide Digital Adoption g. virtual office, virtual stores, virtual retailers
- CAPEX/OPEX Optimisation: Operator CAPEX is on the rise, so this is the key area which could differentiate a successful DSP from an unsuccessful one.
Operators can efficiently plan their network design by segmenting customers according to their daily travel plans. This will help them evaluate and update their geographical networks in order to optimise the network spend and provide better customer service. This would significantly increase their customer engagement, reduce the cost of network deployment and reduce CAPEX.
Re-defining the digital customer journey
Let us illustrate how the digital customer journey can be re-defined by operators with the help of a scenario
Mr Sharma has two postpaid connections and n active user of internet and mobile banking. His wife also has a postpaid connection in her name. She has been browsing websites on international holiday destinations and actively liking Facebook travel/tourism pages. While a CSP pitches international roaming packages to his wife based on her browsing history, a DSP creates an exhaustive, comprehensive view of customer i.e. the persona of Mr Sharma by incorporating household, account, transactions, social media feeds, positive/negative sentiments, etc. to determine from Mrs. Sharma’s web browsing history that the entire family is going on an international vacation and identifies personalized cross-sell up-sell opportunities e.g. selling Travel Insurance through mobile banking apps.
A successful DSP will also incorporate insights based on customer-customer relationships and householding information in their product recommendations. Mr Chopra works in the same department as Mr Sharma and is also likely to take an international vacation. Here the DSP can cross-sell International Roaming Offers, International Data pack offers, Travel Insurance to Mr Chopra as well.
The key to increasing customer engagement in this age of digital transformation is obtaining a comprehensive view of a customer by creating a digital customer journey map which helps operators pitch personalised product/services to their customers. The first step in developing a Customer journey map is developing a “persona” for the digital customer to map his expectations and experiences at each stage of his life cycle.
Insights generated from this digital persona about specific customer traits, positive/negative experiences, browsing history, online behavioral patterns/trends can be incorporated into the existing Cross Sell-Up Sell/Customer Retention Models in order to identify the various digital touchpoints (website, email, and social media, mobile) through which contextual offers can be pitched to the customers who are more profitable. This will also enable the operators to optimise the marketing spend on campaigns.
Technology Approach
Some of the key tools and technologies which will be used in the transition from a CSP to a DSP in the next few years are
- Natural Language Toolkit
NLTK provides easy-to-use interfaces for building Python programs to work with human language data. It provides over 50 corpora and lexical resources such as WordNet, along with a suite of text processing libraries for classification, tokenization, stemming, and tagging, parsing, and semantic reasoning.
- Machine Learning
Machine learning algorithms operate by building a model based on inputs and using that to make predictions or decisions, rather than solely obeying explicitly programmed instructions.
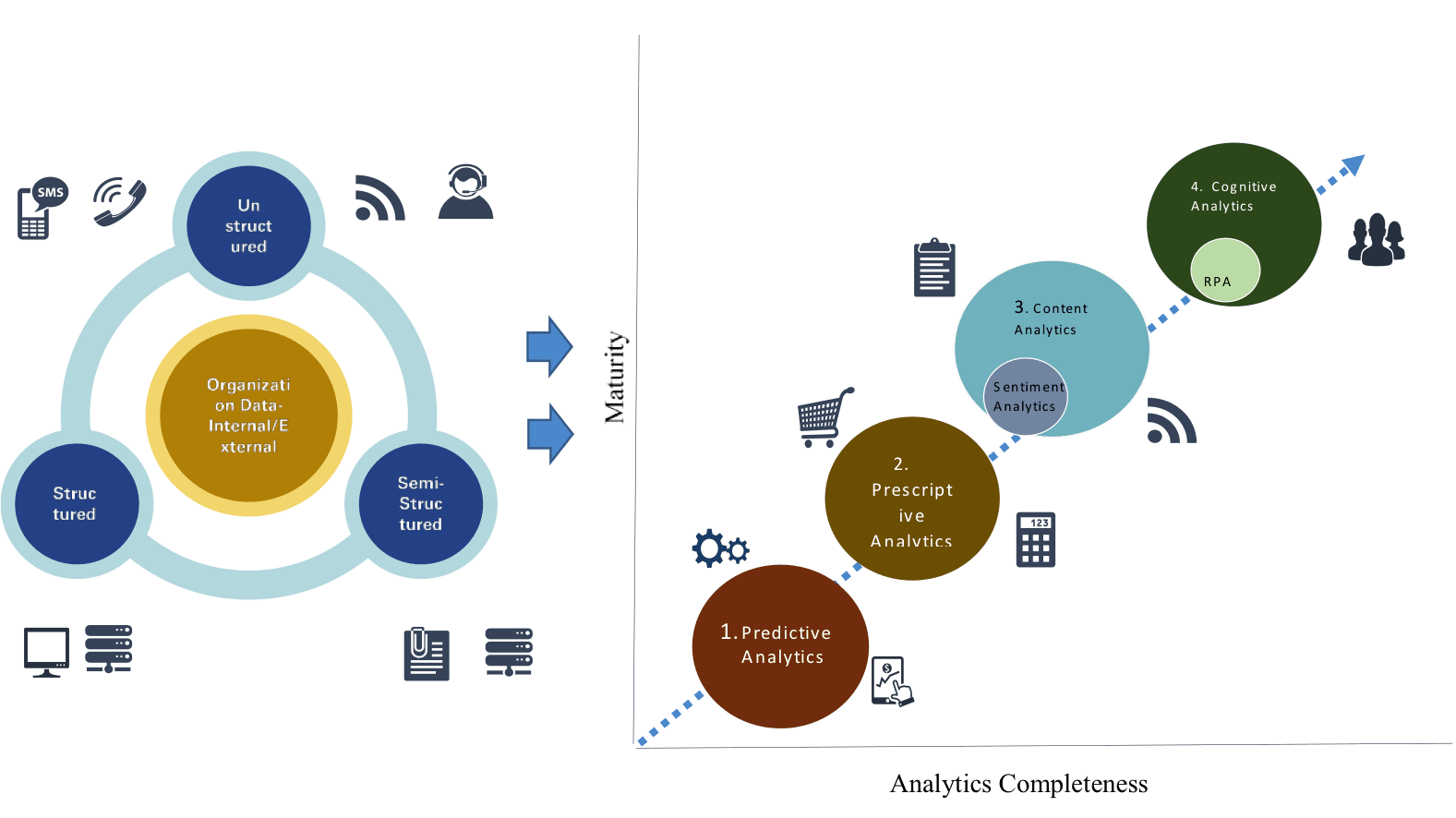
As CSPs are increasingly adopting an enterprise-wide Digital Transformation strategy, they are moving towards Maturity Level 3.0 i.e. Content Analytics which includes Sentiment Analytics using NLP, text analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI). While organizations in maturity level 2.0 use data-driven insights from their conventional analytical models to take business decisions, a transition to level 3.0 requires incorporation of insights from the vast amounts of unstructured internal/external data in the existing analytical models in order to understand the interrelationships between key drivers better, identify key pain points and get an integrated view of their business.
This will enable them to arrive at more efficient and sustainable business decisions as compared to level 2.0. Moving beyond Level 3.0, organisations can use the text data for Cognitive Analytics & Robotic Process Automation (RPA) e.g. extracting competitors’ pricing data from their websites.
Conclusion
The path to becoming a successful Digital Service Provider from a Communication Service provider is fraught with the increasing challenge from OTT players & new startups like Uber, Netflix, Spotify, Airbnb, Skype, who with their disruptive platform-based business models are putting CSPs under tremendous pressure by targeting their core services and consuming the bandwidth.
It will be imperative for the operators to respond to the increasing challenge by launching innovative services, particularly in the areas of mobile money and machine-to-machine (M2M) services e.g. launching new voice calling, messaging apps , own content/video platforms. NLP, and Text Analytics, Machine Learning and RPA will prove to be the key pillars to this disruptive transformation in the next few years.
This, along with building a sustainable partner ecosystem by providing Data as a Service and opening up alternate monetization avenues will significantly improve both the top line along with the bottom line and enable the operator to maintain a competitive advantage over other players in the long run.
Authors
 Somnath De, Technical Director, Data & Analytics, KPMG
Somnath De, Technical Director, Data & Analytics, KPMG
Somnath is a Director in the Data & Analytics practice of KPMG, India and leads the D&A initiatives. He has over 18 years of consulting experience and has undertaken multiple Data Science engagements for leading organizations across multiple industry sectors like Telecom, Manufacturing, Utilities, Financial services. He actively participates in digital and data &analytics events/panel discussions conducted by leading educational institutes and major newspapers
 Saibal Samaddar, Associate Director, Data & Analytics, KPMG
Saibal Samaddar, Associate Director, Data & Analytics, KPMG
Saibal is an Associate Director in the Data & Analytics practice of KPMG, India. He has over 10 years of consulting experience in Data & Analytics working for various telecom clients. He has been focusing on strategy & roadmap for Big Data & Advanced Analytics, implementation and consulting in Master Data Management, Data Quality, Advanced Analytics including text analytics for Customer Value Management, Network Analytics, Call Centre Optimization, etc. He holds a Master degree in Electrical Engineering.
 Upasana Mukherjee, Consultant, Data & Analytics, KPMG
Upasana Mukherjee, Consultant, Data & Analytics, KPMG
Upasana is currently working as a Consultant in the Data & Analytics practice of KPMG, India. Upasana holds a Post Graduate diploma in Management from Indian Institute of Management, Indore. She has around 3.5 + years of work experience and has worked in multiple advanced analytics and data science engagements spanning industries like Telecom, Utilities, banking, manufacturing. She has worked extensively on SAS, Big Data, Data Management & Advanced Analytics, R, Tableau, Oracle and SQL.