CVDC 2020, the Computer Vision conference of the year, is scheduled for 13th and 14th of August to bring together the leading experts on Computer Vision from around the world. Organised by the Association of Data Scientists (ADaSCi), the premier global professional body of data science and machine learning professionals, it is a first-of-its-kind virtual conference on Computer Vision.
The second day of the conference started with quite an informative talk on the current pandemic situation. Speaking of talks, the second session “Application of Data Science Algorithms on 3D Imagery Data” was presented by Ramana M, who is the Principal Data Scientist in Analytics at Cyient Ltd.
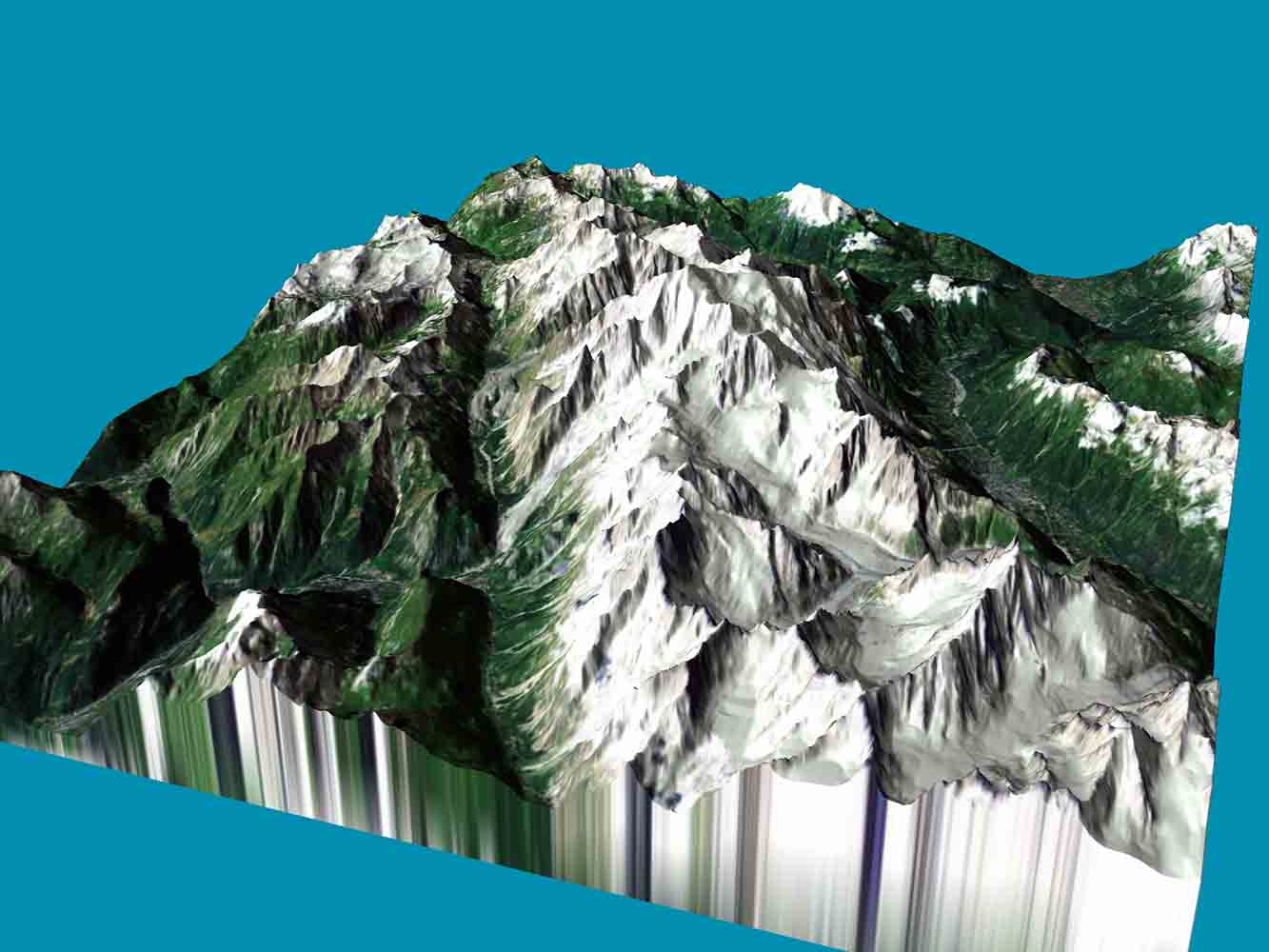
Ramana talked about one of the most important assets of organisations, data and how the digital world is moving from using 2D data to 3D data for highly accurate information along with realistic user experiences.
The agenda of the talk included an introduction to 3D data, its applications and case studies, 3D data alignment, 3D data for object detection and two general case studies, which are-
- Industrial metrology for quality assurance.
- 3d object detection and its volumetric analysis.
This talk discussed the recent advances in 3D data processing, feature extraction methods, object type detection, object segmentation, and object measurements in different body cross-sections. It also covered the 3D imagery concepts, the various algorithms for faster data processing on the GPU environment, and the application of deep learning techniques for object detection and segmentation.
Ramana started the talk by explaining what 3D data actually is and where it can be used. He stated that there are mainly two important requirements, which are- firstly, align the different objects, which is a computationally difficult thing and the second is the detection of the objects.
According to Ramana, the 3D data can be generated using various ways, which include the UAV data, camera and CAD data. Based on different applications there are basically two types of data format, which are-
- Point Cloud data: In a point cloud data, in a 3D view, every pixel is a one-point which is represented in 3-dimensional coordinates. The data format can be 3D coordinates (x,y,z), normals or colours.
- Mesh data: In mesh data, instead of representing data points, it is represented as triangles in 3 dimensions to define the 3D surface. The mesh data is used in any linear design of any mechanical products. The data format can be polygon file format, stereolithography, object files, GL transmission format, among others.
Some of the use cases that Ramana mentioned are-
- In agriculture, it can be used for crop categorisation.
- In autonomous vehicles, it can be used for navigation, collision avoidance, autonomous cruise control and obstacle detection in autonomous vehicles.
- Other use-cases include forestry, bio-conservation, medical imaging, among others.
The applications of 3D data can include frequent airborne surveys by collecting LIDAR data to detect vegetation growth and terrain changes due to weather or constructions for optimal planning and maintaining the power distribution lines or rail network.
It can also be used to build highly accurate autonomous vehicles by analysing 3D point cloud data to detect the objects on the pathways measuring the dimensional changes of the large machinery equipment in mining industries for highly efficient operations.
Popular libraries like Open3D and Point Net++ have been used for the studies. Next, he discussed about the alignment of 3D objects and the steps that are important. The steps include are
- Basic operations, which consists of scaling and transformation-translate and rotations.
- Outlier removal, which includes radius outlier removal or statistical outlier removal.
- Global registration: This step includes algorithms like RANSAC (Random Sample Consensus), random downsampling, nearest neighbour and others.
- Iterative Closest Point (ICP) registration: This algorithm is utilised using point-to-point or point-to-plane.
Further, Ramana explained the steps of object detection of 3D objects, where the main goal includes partitioning of point sets, abstracting local features and farthest point sampling. The talk was concluded discussing the scopes of the case studies, where classification and clustering methods have been used to identify object types.