This article originally appeared in our annual study titled “10 Leading Analytics & Data Science Providers in India 2017”, which was carried out in association with AnalytixLabs. Read the complete study here.
The best jobs right now in the planet include titles like data scientist, data engineer, and business analyst. Yet too often, employers find it hard to acquire the right person for a job. There is a persisting gap between the skills possessed by the current or the emerging workers and the abilities required by the business.
The data science and analytics industry needs personnel with multidisciplinary skill sets. A keen analytical mind with the required technological prowess and business acumen may seem to be the best match for most advanced analytics roles. But along with the varied technical skills the candidates must also possess problem solving skills as well as soft skills like communication, creativity and teamwork. This holistic skill set is rare, so companies will expect to compete fiercely for T-shaped individuals, as they are now often called (those with a principle competency, plus well-honed broad skills to help them cross functions or domains).
There are two broad different families of data science and analytics jobs which we come across in the market.
- Analytics-Enabled jobs
- Data science jobs
Analytics-Enabled jobs:
Common analytics-enabled jobs are Chief Executive Officer, Chief Data Officer, Director of IT, Human Resources Manager, Financial Manager, Marketing Manager, Systems Analyst, Business Analyst (IT), Product Manager, Operations Analyst etc.
The analytics IQ is raised with greater productivity and operational efficiency in mind. These are the people with the know-how to identify what the customer needs using social analytics, or unusual network activity from real-time dashboards, or to forecast inventory using predictive analytics. The analyst at the top of his ability can not only understand but virtually anticipate consumer needs and influence them with the campaigns. It’s not surprising that most of the job openings are analytics-enabled and require functional or domain expertise outside of data science at the core. What analytics-enabled jobs require is hands-on experience with reporting and visualization software to aid in the collection and examination of data.
Data science jobs:
Common Data Science jobs include Business Intelligence Engineer, Data Analyst, Data Architect, Data mining Analyst, Data Base Administrator, Data Engineer, Data Scientist/ Advanced Data Analyst/Analytics Specialist etc. Data science professionals need a different set of competencies and skills. They add bring with them the aptitude that enterprisers and entrepreneurs always desire. Candidates for these roles are supposed to possess strong credentials (either experience or education) in programming and applied data science. It is however, an interesting, deep data pool which is of utmost importance to keep the data scientists and engineers engaged in meaningful work. The other indispensable requirement is a well-organized platform which makes the data available for all available units of the company’s workforce
Typical Expectations from the different roles:
A number of technical and non-technical abilities are expected for both data science and analytics-enabled job roles.
The non-technical skills include:
- Overview of analytics field,
- Basic domain & functional understanding,
- Communication & presentation skills,
- Energy & passion towards job,
- Logical thinking (structural approach, problem solving approach, attention to details, ability to handle pressure etc)
The technical skills include:
- Basic knowledge of Math and Statistics
- Data Base & Big Data concepts
- Statistical programming
- Competence with Statistical & Data Visualization tools
- Machine Learning & Deep Learning
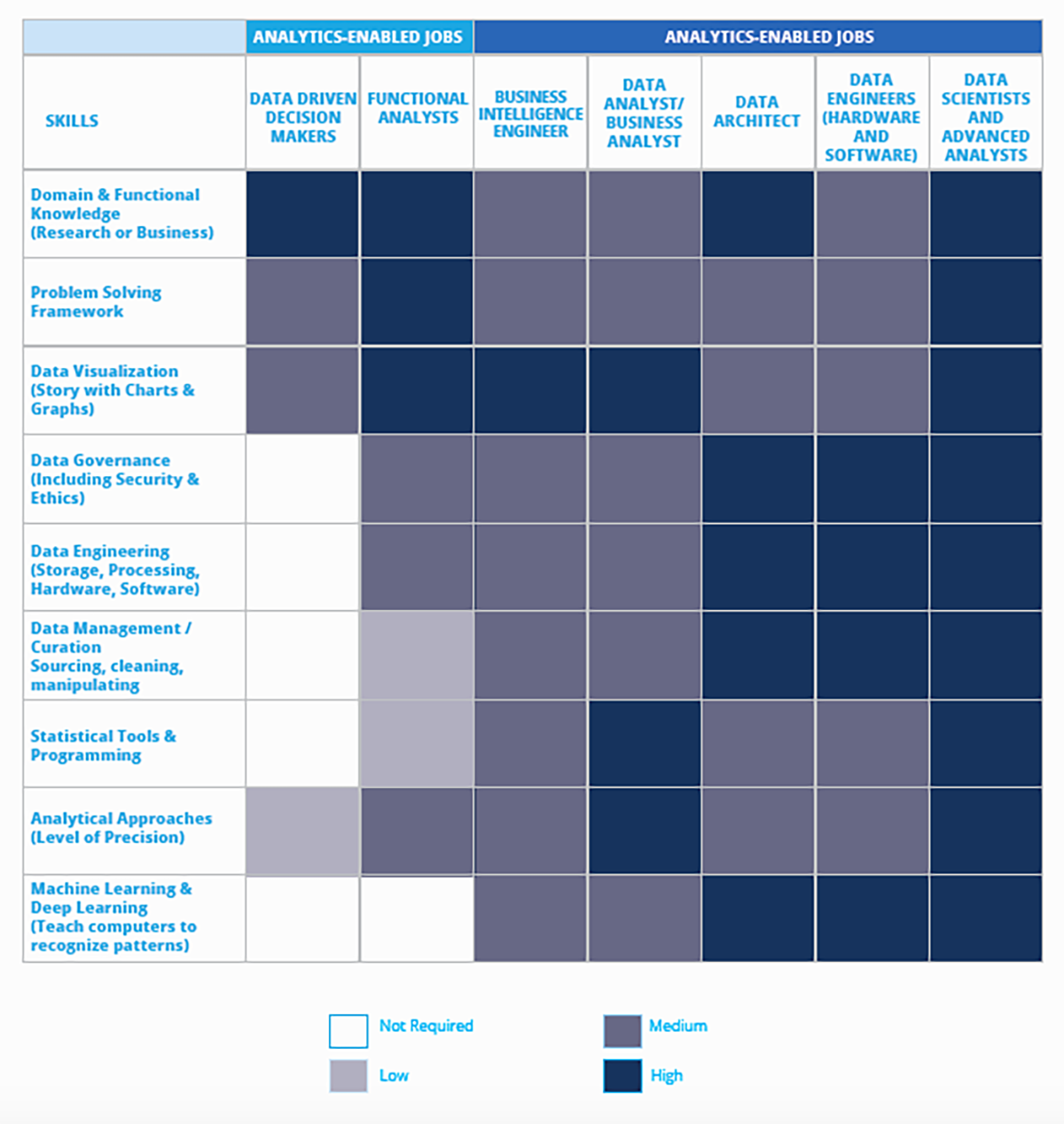
A competency map (as mentioned below) becomes necessary for companies in order to identify the principal competency for each job since there is no common language for using analytics, and different problems require different skills. The candidates need to possess the knowledge and skills required for completing certain operations. They are asked to solve certain problems in order to qualify for the job roles. In this way the employer can ensure that the company’s priorities are served.
Typical expectations from Data Science Jobs:
Business Intelligence Engineer:
- The primary task is to consume historical data from transactional databases; denormalize, flatten, reshape and aggregate the data with the help of tools like SQL/Hive/Pig etc
- Perform some basic statistical analysis
- Build effective and attractive data visualizations (Reports & Dashboards) using visualization tools (Tableau/Power BI)/program to present or communicate the data effectively.
- Preparing dashboards which will be used by senior management and Decision makers.
- These people are not necessarily in possession of strongest technical skills, but they can fill in anyone’s shoes whenever required. This is also a very cross-functional role as you work with data engineers to get the data, data scientists to get statistical analysis done and with business analysts/managers to present the insights.
Data Analyst/Business Analyst:
- The primary role of data analyst/business analyst is compilation and quantitative analysis. They usually have a computer science and business degree. They are tasked with getting out analytical insights of the bulk of data available to the organization. These insights, compiled into decent reports, should make sense to the non-technical counterpart of the company helping them decide their course of action.
- An analyst’s job profile might require basic statistics although it does not usually require advance statistics and has nothing to do with “Big Data” in particular.
- A well-established organization can have multiple analysts with different roles. For example – an operations analyst may look at operational & productivity metrics of different resources and figure out a strategy to improve operations efficiency and communicate the report to the leadership.
Data Architect:
- Large enterprises generate huge amounts of data from various sources. The Data Architect is someone who can understand all the sources of data and work out a plan for integrating, centralizing and maintaining all the data.
- Data Architects must be able to understand the relevance of the data in hand with regard to the current operations of the organization and also the how the handling and effectiveness of the data may change with future changes in the organizations work process.
- Data Architect needs to have an end-to-end vision. It is important to understand the translation of a logical design into one or more physical Databases. They also recognize the flow of data through different stages.
- The job role may include things like designing relational databases, developing strategies for data acquisitions, archive recovery, and implementation of a database, cleaning and maintaining the database by removing and deleting old data etc.
Data Engineer:
- These are competent engineers who know the internals of database software.
- Data engineers are assigned with a myriad of critical tasks like compiling and installing database systems, writing complex queries and scaling them to multiple machines, ensuring backups and putting disaster recovery systems in place.
- Data Engineers are usually required to have a deep knowledge of and expertise in one or more different database software like SQL, NoSQL, and/or Big Data Frame works like Hadoop & Spark etc.
Data Scientist:
- “Data Scientist” is a topical phenomenon. The general mission of a data scientist is similar to that of an analyst – drawing insights out of data. But once the volume and velocity of the data scales beyond a certain limit, getting effective insights requires a fairly sophisticated skill set.
A “Data Scientist” usually has many overlapping skills – Database Engineering, handling Big Data systems, knowledge of statistical programming languages, business knowledge and knowledge of statistics or data mining. - Unlike a traditional analyst who is likely to look at data from a different source a data scientist looks into data from different sources to get better perspective.
- The data scientist will ideally sift through the massive influx of data in order to find the hidden insight that might help the business to strive forward.
- Good data scientists have keen business acumen. They do not just try to solve the problem at hand but also pick up problems the solution of which can help the organization in long run.