ClearML is an open-source, zero-integration machine learning/deep learning experiment manager and ML-Ops solution. It integrates using just two lines of code. Additionally, like GitHub, ClearnML has version control, but without worrying about conflicts, commit issues. The scalable design of ClearML aims to help developers and researchers manage complex projects with minimal integration effort. It comes with a plethora of helpful functionalities such as:
- Saving ML models and datasets that can be shared on cloud storage systems.
- Displaying a summary of python packages used in experiments with their specific version.
- Web UI for remotely stopping, monitoring, and running experiments.
The Python package integrates ClearML into your existing code using two lines of code. The ClearML server stores experiments, models, and workflow data, and the Web UI experiment manager. It is available as a hosted service and open source for you to deploy your own server. ML-Ops orchestration is done by the ClearML agent that can be on a remote system.
Installing and setting up ClearML client and agent
To run a client you need to register an account on a ClearML-server here. You’ll be prompted to create credentials in the getting started screen, generate them, and copy them to your clipboard for later.
Install clearml client
pip install clearml
To configure the client run
clearml-init
Paste the credentials you generated earlier and confirm the default configuration for the Host, Web App, API, and Filestore.
Integrating with two lines of code
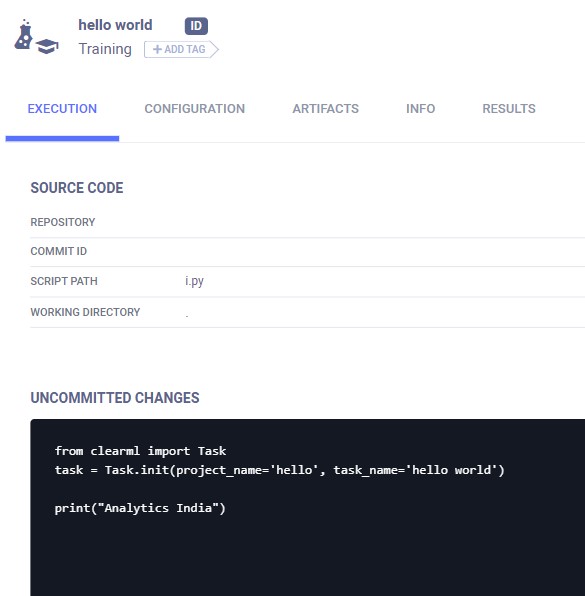
from clearml import Task
task = Task.init(project_name='hello', task_name='hello world')
print("Analytics India")
When this is run, the output is not only printed on your machine but also logged in the server.
An agent is needed to run experiments, pipelines, and automation. Remember, we ran the hello world task locally on our system. The agent should be installed and configured on the machine you want it to run.
pip install clearml-agent
Configure the agent just like the client.
clearml-agent init
Start the agent in foreground mode. This means the agent will print the output to the screen. In actual service mode, the output will be stored automatically into a temporary file.
clearml-agent daemon --queue default --foreground
Creating a simple ML pipeline using ClearML
We’re going to create a very basic pipeline with three stages- The first stage will upload the dataset artifact, the second stage will process the data, and the final stage will create and train the model.
Create experiment tasks corresponding to the three stages
- Downloading the data and storing it as an artifact named dataset(stage_one.py)
from clearml import Task, StorageManager
task = Task.init(project_name="pipeline", task_name="pipeline step 1 dataset artifact")
# only create the task, it will be executed remotely later
task.execute_remotely()
# simulate local dataset, download one, so we have something local
local_iris_pkl = StorageManager.get_local_copy(
remote_url='https://github.com/Aditya1001001/machine-learning-basics/blob/master/iris_dataset.pkl')
# add and upload local file containing the dataset
task.upload_artifact('dataset', artifact_object=local_iris_pkl)
print('uploading artifacts in the background')
print('Done')
- Getting the data from the previous task, processing it, and uploading the processed data(stage_two.py)
import pickle
from clearml import Task, StorageManager
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
Task.init(project_name="pipeline", task_name="pipeline step 2 process dataset")
# Use either dataset_task_id to point to a tasks artifact or
# use a direct url with dataset_url
args = {
'dataset_task_id': '',
'dataset_url': '',
'random_state': 42,
'test_size': 0.2,
}
# store arguments, these will be changed in the cloned task when the pipeline is run
task.connect(args)
print('Arguments: {}'.format(args))
# only create the task, we will actually execute it later
task.execute_remotely()
# get dataset from task's artifact
if args['dataset_task_id']:
dataset_upload_task = Task.get_task(task_id=args['dataset_task_id'])
# download the artifact
iris_pickle = dataset_upload_task.artifacts['dataset'].get_local_copy()
# get the dataset from a direct url
elif args['dataset_url']:
# simulate local dataset
iris_pickle = StorageManager.get_local_copy(remote_url=args['dataset_url'])
else:
raise ValueError("Missing dataset link")
# open the local copy of the dataset
iris = pickle.load(open(iris_pickle, 'rb'))
# "process" data
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=args['test_size'], random_state=args['random_state'])
# upload the processed data
print('Uploading process dataset')
task.upload_artifact('X_train', X_train)
task.upload_artifact('X_test', X_test)
task.upload_artifact('y_train', y_train)
task.upload_artifact('y_test', y_test)
print('Notice, artifacts are uploaded in the background')
print('Done')
- Creating, training, and storing the model(stage_thrre.py)
import joblib
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from clearml import Task
task = Task.init(project_name="pipeline", task_name="pipeline step 3 train model")
# This will be changed in the cloned task when the pipeline is run
args = {
'dataset_task_id': '',
}
task.connect(args)
task.execute_remotely()
print('Retrieving Iris dataset')
dataset_task = Task.get_task(task_id=args['dataset_task_id'])
X_train = dataset_task.artifacts['X_train'].get()
X_test = dataset_task.artifacts['X_test'].get()
y_train = dataset_task.artifacts['y_train'].get()
y_test = dataset_task.artifacts['y_test'].get()
print('Iris dataset loaded')
model = LogisticRegression(solver='liblinear', multi_class='auto')
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
joblib.dump(model, 'model.pkl', compress=True)
loaded_model = joblib.load('model.pkl')
result = loaded_model.score(X_test, y_test)
print('model trained & stored')
print('Done')
Run the three stages in order to create the base task in the server.
Create a pipeline, add the three stages and run it(controller.py).
from clearml import Task
from clearml.automation.controller import PipelineController
# Connecting ClearML with the current process
task = Task.init(project_name='pipeline', task_name='pipeline demo',
task_type=Task.TaskTypes.controller, reuse_last_task_id=False)
# Creating the pipeline
pipe = PipelineController(default_execution_queue='default', add_pipeline_tags=False)
# Adding the first stage to the pipeline, a clone of the base tasks will be created and used
pipe.add_step(name='stage_data', base_task_project='pipeline', base_task_name='pipeline step 1 dataset artifact')
# overriding the arguments of the second stage(adding the first stage’s task_id) before and adding it to the pipeline
pipe.add_step(name='stage_process', parents=['stage_data', ],
base_task_project='pipeline', base_task_name='pipeline step 2 process dataset',
parameter_override={'General/dataset_url': '${stage_data.artifacts.dataset.url}',
'General/test_size': 0.25})
# overriding the arguments of the the third stage(adding the second stage’s task_id) and adding it to the pipeline
pipe.add_step(name='stage_train', parents=['stage_process', ],
base_task_project='pipeline', base_task_name='pipeline step 3 train model',
parameter_override={'General/dataset_task_id': '${stage_process.id}'})
# Starting the pipeline
pipe.start()
# Wait until pipeline terminates
pipe.wait()
# cleanup everything
pipe.stop()
print('done')
Note that the base tasks are not executed, they are first cloned, and then the clone tasks are executed.





















