In our previous articles, we have talked about Time Series Forecasting and Recurrent Neural Network. We explored what it is and how it is important in the class of Machine Learning algorithms. We even implemented a simple LSTM Network to evaluate its performance on the MNIST dataset. In this tutorial, we will take it a little further by forecasting a real-world data.
The cryptocurrency market has seen its rise and fall in the past few years. With a variety of coins being exchanged for real money, it is important to know the trend in the coin price. In this article, we will build a fairly simple LSTM network to predict or forecast the prices of Bitcoin.
Obtaining Bitcoin Data
There are plenty of open sources available on the internet to extract historical data of Bitcoin prices. The one that I have used below is from Coinmarketcap.
You can view and download the dataset here.
Loading And Understanding The Data
Importing Necessary Libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
Importing The Dataset
complete_data = pd.read_excel('BitCoin_Prices.xlsx')
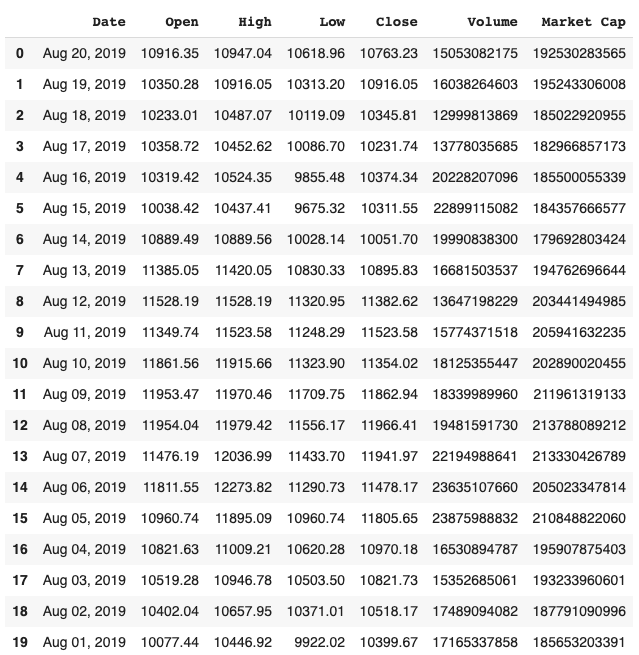
print(complete_data.head(20))
Output:
The dataset consists of 7 features. This is how most of the stock information datasets will look like.
- Market Capitalisation/Market Cap: It is the total dollar market value of a company’s (in this case Bitcoin) outstanding shares.
- Volume: The total amount of security that changes hands over a given period of time (In this case the time period is one day)
- Close: The closing price of the stock(Bitcoin price at the end of the day).
- Low: Low denotes the lowest value or drop over the complete time period.
- High: The highest value or rise over the complete time period.
- Open: The opening price of the stock of a particular day.
- Date: The date of observation.
In this use case, we will predict the closing price of Bitcoin on a particular day, given the prices of Bitcoin over the past few days.
Let’s code!