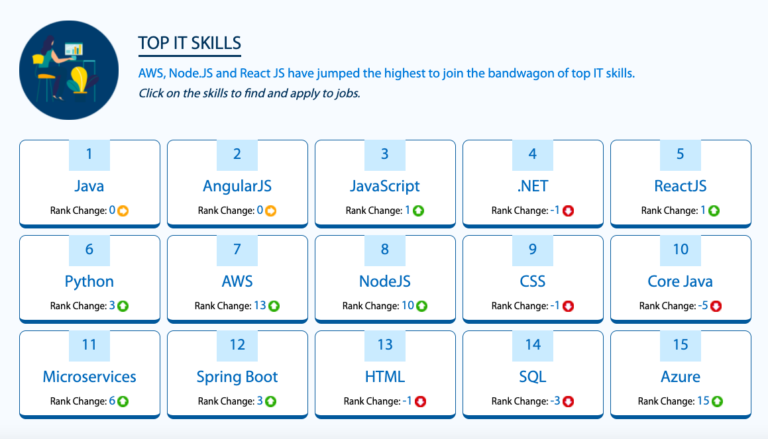
The Government of India has been making a concerted move towards the building future with relevant skills in a rigorous and continuous manner for lifelong learning. In fact, the recent policies are also showcasing that the Government is paying close attention to the kinds of skills — especially in the technology area — which will be imperative to the future.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s flagship scheme, Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) has till date seen about 50 lakh people getting skilled and prepared for a new successful India.
Apart from traditional skills and trades, the PMKVY has also showcased a keep interest in upskilling the Indian talent to more industry-ready jobs, especially in the emerging tech sector. Here are the key roles listed under the PMKVY draft:
IoT And Smart Agriculture
With almost 70% of the Indian population depending on agriculture and its services and around 75% of the population residing in rural areas, agro-based economies like India are a typical realm for applicability of smart agriculture. The improving accessibility of low-cost IoT sensors and affordable solutions for smart agriculture has mitigated the challenges associated with the adoption of IoT-based big data analytics in agriculture to a large extent.
Smart agriculture encompasses a number of applications. Some of the best -known use cases of this concept are as follows:
- Precision Farming: A practice or process followed for improving the accuracy and control over farming and livestock management is commonly referred to as precision farming. Typically, this practice makes use of automated hardware, sensors, robotics and control systems, in addition to other technologies, to achieve its purpose. Precision farming continues to be the most popular application of smart agriculture.
- Smart Greenhouses: In these setups, the microclimate is controlled and monitored to ensure optimal plant growth. Some of the smart agriculture solutions that support this capability include Growlink, Farmapp and GreenIQ.
- Farm Management Systems: A number of IoT devices can be installed on the premises for measuring different farm parameters for collecting data. Analytics are performed on this data and reported via a dashboard. These systems are also referred to as farm productivity management systems. Logistics, storage management and vehicle tracking are some of the best examples of this use case. Commercially available solutions belonging to this category include Cropio and FarmLogs.
One of their recent solutions uses satellite imagery, IoT, weather forecasting and artificial intelligence-based image processing for evaluating the presence of diseases and pests in large areas. Moreover, predictive analytics related to the same are also provided.
Drone Technology
The Ministry of Civil Aviation has been working for several years to establish a world-leading drone ecosystem in India. To that end, it was necessary to develop global standard drone regulations that would permit, will appropriate safeguards, the commercial application of various drone technologies.
The Ministry is now set to allow the commercial use of drones as taxis and delivery vehicles, and permit their operation beyond the visual line of sight under its Drone 2.0 policy, which is likely to take effect by March 2019 and open up a raft of business opportunities.
Drones can be put to excellent use in applications where manual inspection is either tedious or inefficient. For instance, in the agricultural industry, drones can be incorporated in agricultural systems for applications like soil analysis, field evaluation, planting, irrigation and assessment of crop health. The use of drones provides immense control to the farmer in terms of the field, altitude and resolution of ground, the farmer wants to survey. Therefore, drones basically collect data, which can later be used for yield prediction, plant counting, measurement of plant height and health indices, drainage mapping and canopy cover mapping, in addition to many others.
Geoinformatics
National Centre of Geo-Informatics will be one of its kind GIS platform for collaborating GIS data source, location-based analytics and Decision Support System serving to Central/State government and departments across the country.
National Centre of Geo-Informatics’ main objective is to provide a national platform for developing geo-informatics related resources and capabilities in the country.
Applications of Geo-Informatics:
- Urban planning and land use management
- In-car navigation systems,
- Environmental modeling and analysis
- Meteorology and climate change,
- Oceanography and coupled ocean and atmosphere modelling,
- Architecture and archaeological reconstruction, telecommunications,
- Biodiversity conservation and maritime transport.
So, a person skilled in GIS can apply his/her skills in a multitude of domains and contribute to establishing India’s goal to become a global hub for advanced technology.
PMKVY By The Numbers
The objective of PMKVY’s Skill Certification Scheme is to enable a large number of Indian youth to take up industry-relevant skill training that will help them in securing a better livelihood. Individuals with prior learning experience or skills will also be assessed and certified under Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL).
Approved for another four years (2016-2020) to benefit 10 million youth Allocated Budget ₹12,000 crores.
Under the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
- 2016-20, as on 24.01.2019, 37.32 lakh (appx.) candidates have been trained under Short Term Training (STT)
- (25.25 lakh), Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) (11.27 lakh) and
- Special Project (0.8 lakh) in various sectors across the country.
- One of the flagship schemes is ‘Craftsmen Training Scheme’ being implemented through a network of 15,042 Industrial Training Institutes.
Outlook
Directorate General of Training (DGT), Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) is entrusted with the responsibility of long term vocational training in the Country.
Since the initiatives and roadmap are laid out, work needs to be done at the grassroots level. This includes providing high-quality secondary education to prepare the population to embrace skills which require relatively higher analytical skills. It is of high importance that the training institutions are held equally accountable along with the policymakers.