During the initial rise of emerging technologies such as AI and ML being used by organizations such as Google and Facebook, most of the compute power for the training and inference of their models came from Graphic Processing Units.
During the initial rise of emerging technologies such as AI and ML being used by organizations such as Google and Facebook, most of the compute power for the training and inference of their models came from Graphic Processing Units.
These are more commonly known as graphics cards, and are suited for training and inference as these are parallelizable workloads. GPUs have thousands of cores and can process multiple facets of the same task in parallel, allowing for a performance gain orders of magnitude higher than what was being seen.
Fast forward to today, where data centers are filled with enterprise grade GPUs produced largely by chipmaker Nvidia, who has pioneered the use of GPUs for accelerating AI models. However, a new trend is on the rise, and it is one that could create a new market and deal a devastating blow to Nvidia’s enterprise sales: Inference chips.
Inference is a part of using ML, and is the term given to the process of making predictions using a ML model that has been trained. This takes up over 90% of the compute costs of running the model, which leads to many inference-grade models to be optimized to function on the lowest amount of compute. GPUs are still widely used for compute due to their parallelization capabilities, but companies are beginning to create inference-only chips.
Some of the biggest companies in the world are entering the market, hoping to catch a slice of something that might as well be the next big thing in computing. Even as GPUs can be used today, the increasingly complex nature of models today and their increased compute cost will bring it to a point where most models cannot run on consumer grade hardware. These companies are aiming to lay the foundation for a consumer-grade product that fits in with existing systems.
These new chips are also scalable, as they are built with the express purpose of providing large amounts of compute power in a small form factor. These are also similar to the cloud TPUs offered by Google. However, those are Application Specific Integrated Circuits for use with ML models. They accelerate every step of the process, and were developed by Google to reduce their dependencies on chipmakers like Nvidia.
Among the companies investing in these technology are Intel, Alibaba and Amazon Web Services. In this article, we will take a look into whether these chips are the future of AI compute.
Alibaba Announces Chipmaker Subsidiary
Alibaba, one of China’s championed tech companies, announced in September last year that they will set up a dedicated chip subsidiary in the second half of 2019. It was announced that the subsidiary would develop an AI inference chip to be used in autonomous driving, smart cities and logistics.
This announcement came after Alibaba began expanding their chipmaking capabilities. In April of 2018, the company acquired a microchip manufacture known as Hangzhou C-SKY Microsystems to ensure the infrastructure of their IoT efforts.
This was due to mounting tensions regarding the trade war with US, as China needed to control it to avoid over-reliance on imports from US. Alibaba routinely helps the Chinese government lay the infrastructure for widespread AI adoption. These will also power most of their new initiatives such as cutting-edge transport and health AI systems.
Amazon Announces Inferentia, Bakes In Support With AWS Services
In November of last year, Amazon announced that they would begin offering machine learning inference chips designed to deliver high performance at low cost. These chips are known as AWS Inferentia, and were announced with support for TensorFlow, Apache MXNet, and PyTorch as well as models that use the ONNX format. Reportedly, AWS users can reduce the costs associated with inference by upto 75% by attaching inference acceleration powered by Inferentia.
The Inferentia chip was stated to be for applications that required a high throughput, low latency inference performance at an extremely low cost. Each of these chips reportedly provide hundreds of tera operations per second, thus allowing complex models to make fast predictions.
The chip also came with seamless integration with Amazon EC2 and Amazon SageMaker instances, allowing developers to integrate external GPU power with no code changes. This can be done using Amazon’s Elastic Inference product, which allows developers to choose just the right amount of inference acceleration for their models.
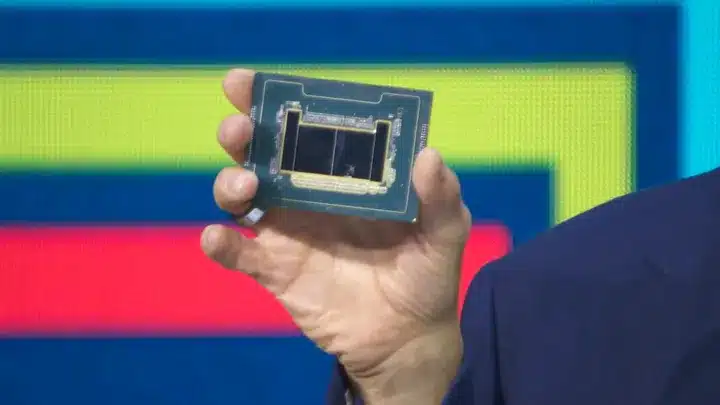
Intel Announces Nervana At CES 2019
At the Consumer Electronics Show this year, Intel, the market leader in CPUs, announced a NN chip for inference workloads. This can be seen as the company’s effort to capture a part of the market it missed out on the first time around. After being overtaken by Nvidia on the AI compute front, Intel seems to be playing catch up to get a slice of the AI pie.
The product is known as the Nervana Neural Network Processor (NNP-I), and fits into a GPU-like form factor. Reportedly, it can deliver up to 10x the training performance of GPUs. Built on a 10-nm process, the processor will include Ice Lake cores for neural network acceleration. It also features the direct management on on board memory by software, and achieves high parallelism by distributing parameters across multiple chips.
The new processors also come with a feature known as Flexpoint that makes multiple chips act as one large virtual chip for accommodating larger models. To also ensure a healthy developer base is working on any problems that can be faced in the real world, Intel partnered with Facebook as a developer partner on this project.
Facebook Dips It’s Toes
Facebook is one of the Internet’s biggest users of AI technology today. Due to the need to deliver over 2 billion curated news feeds, the company adopted the widespread usage of AI predictive technologies built to increase engagement on the platform.
They are one of the biggest customers for any specialized hardware that can make this process faster and more efficient. While not only entering into a developer partnership with Intel, Facebook introduced Glow, a compiler that provides a variety of optimizations to accelerate inference performance.
Facebook is looking to proliferate deep learning frameworks such as PyTorch with this compiler, and also support it on a range of hardware platforms to support a growing number of AI and machine learning industry needs.
Conclusion
The move of industry players towards creating inference-only chips can represent the move of the industry as a whole. While the specialized systems we have today are likely to stick around for consumer use, enterprises will continue to look for ways to optimize their AI divisions. The rise of consumer-grade inference chips might as well speed up the rise of AI worldwide.