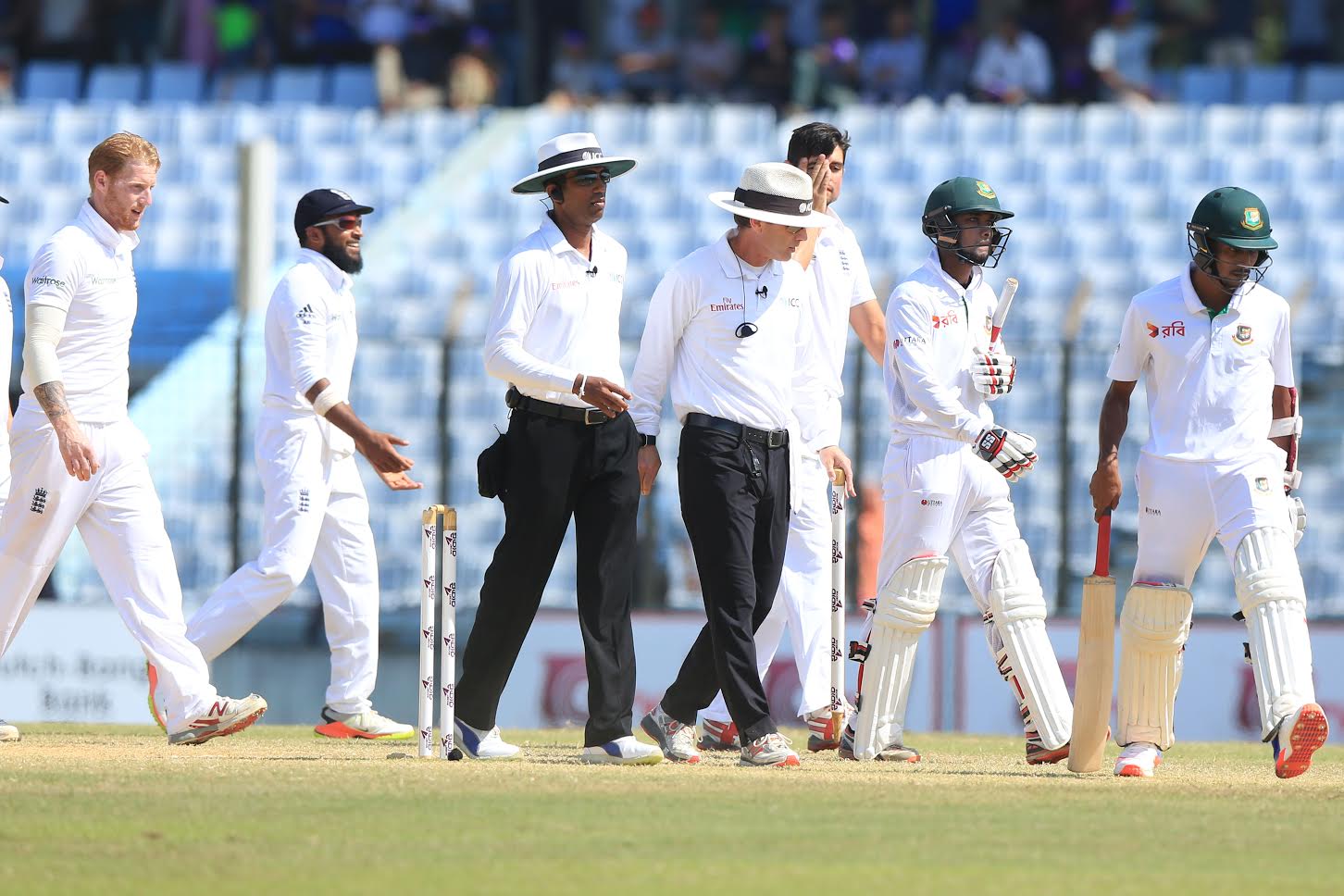
Sports technology has changed the face of international cricket with objective umpiring, fan engagement ruled by AR & VR and smart wearables driving on-field and off-field player and team performance. There’s a slew of tech applications that comes handy in objective umpiring as well.
Just like football, cricket has also developed and integrated several game-changing technologies over the years. Although, ICC have been rightly cautious about making changes to the game, as those could impact both players and the game itself. While Decision Review System, or DRS as it is more popularly called, first introduced in 2008 has become the go-to technology for assisting umpires, there is a host of other tech innovations as well.
Today, international cricket incorporates the use of sensors and several data analytics tools which help the on-field umpires to conduct a fair game.
Unlike other games, the referral from the DRS has to be adjudicated by the third umpire. The system allows players to challenge any decisions made by the on-field umpires. But each team is limited to three unsuccessful challenges per innings. The referral system is a great step forward for cricket.
Snickometer

Televised cricket today makes extensive use of this tool to graphically analyze sound and video. Sniko also shows the noise frequency to determine whether the ball touched the bat before going to the fielder.
British computer scientist Allan Plaskett had invented and introduced Snickometer in the mid-90s, and since then the technology has been instrumental in aiding umpiring decisions. It uses a very sensitive microphone located in one of the stumps, that picks up the sound when the ball nicks the bat. Moreover, third umpires used the Snickometer frequently to take decisions on a complex catch appeal.
Role of Analytics: The live sound is recorded by the stump microscope, which is filtered and relayed to an oscilloscope. The relevant sound waves are traced by the oscilloscope. Next step involves profound analysis on the footage recorded. A single, sharp spike on the graph confirms the ball touching the bat. On the other hand, a flatter impact implies that the ball either touched the pad or the glove. Analysis done using the Snickometer really turns useful when the Umpire has to take really close call.
Hot Spot

The Hot Spot was introduced in cricket as an alternative to Snicko. The technology addresses the inconsistencies noticed in case of a Snickometer. The technology utilizes an infra-red imaging system to determine where the ball struck before reaching the fielder. The technology improves the on-field umpire’s decision-making accuracy. Moreover, the technology is also used primarily as an analysis aid for televised coverage.
Hot Spot technique essentially relies on two infra-red cameras positioned on either end of the ground and. These cameras measure the heat generated by a collision, such as ball on pad, ball on bat, ball on glove, or anywhere else.
The technology uses a subtraction technique. A series of black-and-white negative frames is generated into a computer, precisely localizing the ball’s point of contact. The infra-red image shows a bright spot where contact friction from the ball has elevated the local temperature.
Role of Analytics: Detecting edges becomes an easier task leveraging Hot Spot, as it’s not a sound-based edge detection system. The analysis done on visuals and infra-red images indicates the area that contacts the ball, through the bright spot. Thus, it proves more useful than Snickometer.
Hawk Eye (UDSC)
Named after its developer Dr Paul Hawkins, this revolutionary technology is not just used in cricket, but it also finds extensive use across other sports such as tennis, soccer, hurling, and more. The technology is built to visually track the ball, and display a record of its statistical path through movie image. The system was originally implemented in 2001 to make television broadcast more interactive.
Hawk Eye technique makes use of six or seven robust cameras that track the ball trajectory from different angles. The video obtained from all the cameras are triangulated and merged to furnish a three-dimensional representation of the ball trajectory.
The technique is accurate to within 5mm (0.19-inch). It helps the empire by observing where the ball pitched, location of impact with the batsmen’s leg, and projected path of the ball past batsman. Most often, Hawk Eye technology is used as part of the DRS for adjudicating LBW decisions. However, it is generally trusted as an impartial second opinion in Cricket.
Role of Analytics: The technology models the trajectory of the ball bowled to determine if the ball would have hit the stumps. For each delivery, the users ‘freeze’ action as soon as the ball pitches, and utilize Hawk-Eye to predict its trajectory. Furthermore, the experiment is carried out at different cricket grounds, with different cricket balls, with different pitch wear and tear, and in different climatic conditions. This helps in making the Hawk Eye analysis more robust and efficient.
PitchVision

This analytics-based cricketing technology was developed by miSport, a UK-based company. The technology can be leveraged by the entire spectrum of Cricket users to provide players key performance feedback. The technology has so far been extensively used in the cricket training system.
Besides, PitchVision enables bowlers to measure and record bowlers pace, line, length, deviation, bounce, and foot position on bowling crease, ball by ball. With the help of this technology, it becomes easier to show the map of bowler’s line and length.
Furthermore, the technology allows batsman to see whether their shots would have pierced the field, identify which specific deliveries get you in trouble, and compare performance against different bowlers.
Role of Analytics: Pitch Vision plays an important role to enable video analysis. This helps to confirm certain suspicions about aspects related to a live game. Besides, players can be shown their footage with valuable analysis, which helps them to improve their individual skills.
Ball Spin RPM

Another defining technology, it helps in determining the rotation speed of the ball. It helps in showing television viewers how much each ball spins, in case of spinners. The technology integrates a counter which depicts the RPM of the ball, and tells how fast the ball spins. The technology leverages a high speed camera focused on the ball, possibly using the same images that are captured for the Hawkeye system.
Role of Analytics: The real-time analytics that this technology introduces helps in calculating the 3D angular velocity characteristics of a spinning ball. The method can successfully analyse spin rate of rotation, spin direction, and spin elevation angle of a sample of spin bowlers. These factors in fact define the spin bowling performance for a player. The analysis is also utilized to prompt feedback to the bowler.