In today’s era, we are surrounded by different types of photo manipulating filters in our mobile phones, apps…etc. But do you know how they do these images manipulations…..? In the backend, they are using computer vision techniques. Computer vision has a wide variety of applications not only to reduce the human effort but also used for entertainment apps. Many photo editing apps like FaceApp, Instagram filters…etc are using computer vision techniques.
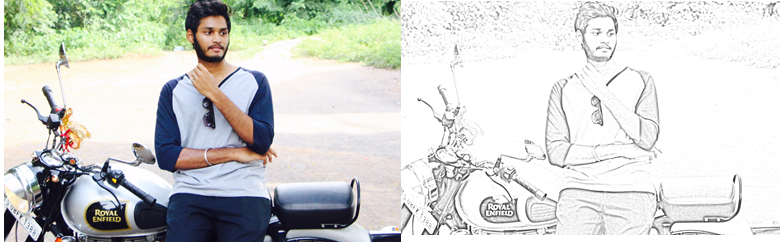
In this article, we will try to convert a normal photo into a pencil sketch using computer vision in a python programming language. In this article, we will show how to convert an image into its corresponding pencil sketch in a few steps.
Step-1: Importing required libraries
from google.colab.patches import cv2_imshow
import cv2
If you are implementing this program in Google Colab, you need to import cv2_imshow from google.colab.patches
Step-2: Loading the image
Using the below code snippet, we will read the image that is to be processed.
img = cv2.imread('/content/pic.jpeg', 1)
cv2_imshow(img)
Step-3: Converting an image into gray_scale image
Using the below code snippet, we will convert the input image into equivalent grey-scale using cv2.cvtColor.
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2_imshow(img)
Converting an image into grayscale gives us black & white pixels in the image which is used for creating a pencil sketch.
Step-4: Inverting the image
Using the below code snippet, we will invert the image color using cv2.bitwise
img_invert = cv2.bitwise_not(img_gray)
cv2_imshow(img_invert)
We are using the bitwise_not function which is used to make brighter regions lighter and vice versa so that we can find the edges to create a pencil sketch.
Step-5: Smoothing the image
In the below code snippet, we will smooth the image using Gaussian Blur.
img_smoothing = cv2.GaussianBlur(img_invert, (21, 21),sigmaX=0, sigmaY=0)
cv2_imshow(img_smoothing)
We have used the gaussian blur technique with 21 x 21 pixel and the default sigma values filter on the image to smoothen our image. By increasing the filter size, we can create thin lines for our sketch and it is used to reduce the noise in the image.
Step-6: Obtaining the final sketch
Using the below code snippet, we will obtain the final pencil sketch of the input image using a blend function dodgev2.
def dodgeV2(x, y):
return cv2.divide(x, 255 - y, scale=256)
By using this function, it is dividing the greyscale value of the image by the inverse of blurred image value which highlights the boldest edges. This technique is used by traditional photographers to print photos from the reel.
Final Output as Pencil Sketch
final_img = dodgeV2(img_gray, img_smoothing)
cv2_imshow(final_img)
Here is the one-by-one transformations from the input image to the output image.
Conclusion
In this article, we demonstrated how to convert our image into a pencil sketch using computer vision techniques in a few lines of code. There are numerous applications in computer vision of obtaining the sketch of an image.