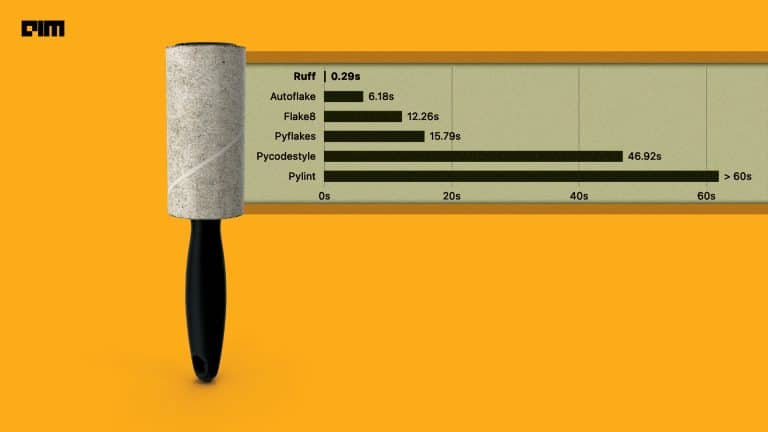
Image processing is performing operations on an image to enhance it or to extract some useful information and to know about the attributes of the image. A systematic study of the image to find out some useful information about that image is known as image processing.
Python allows image processing using different libraries and one of them is Pillow, which is an open-source Python Imaging Library that adds image processing capabilities to your Python interpreter.
Pillow offers all types of capabilities like image transformation, rotation, resizing, statistics of the image, etc. It supports the extensive file format and is designed to fast access the data stored in pixels.
In this article, we explore Pillow and learn about its image processing capabilities.
Implementation:
Like any other library, we will first install pillow using pip install pillow
- Importing required library
We will start by importing Image function from PIL. This function is used to process the image and perform operations on it.
from PIL import Image
- Loading the image
We can work on any image of our choice of any format. I am using an image of a bird that I downloaded from google.
img = Image.open("sparrow.jpg")
img
- Image processing
Lets us start the image processing by knowing the mode, size, and the format of the image.
- Basic Properties
Pillow has inbuilt functions to know the basic properties of the image. Lets us see how we use them to draw some information.
print('Format:',img.format)
print('Size',img.size)
print('Mode:', img.mode)
- Cropping the Image
In the cropping section, we will crop the image by creating a box of a particular size and cut it out of the image.
box1 = (200, 200, 800, 800)
crop1 = img.crop(box1)
crop
As you can see according to the size of the box we have a cut out from the image which is the cropped version.
- Splitting the Image
As we already know from above that the image is in RGB mode, in this step we will split it into ‘L’ mode i.e. a single channel Luminance.
R, G, B = img.split()
R
The image is split into three parts with a single channel ‘L’.
- Transformations
Let us analyze different transformation functions. Starting with resizing the image.
- Resizing
resized_image = img.resize((256, 256))
resized_image
- Rotating Image
rotated_image = img.rotate(90)
rotated_image
- Transposing Image
tran_image = img.transpose(Image.FLIP_TOP_BOTTOM)
tran_image
- Changing color
img1 = im.convert('1')
img1
- Filters
Let us analyze different filters that are defined under the Pillow library.
- Blur Image
from PIL import ImageFilter
blurred = img.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)
blurred
- Sharpen Image
sharped= img.filter(ImageFilter.BLUR)
sharped
- Finding Edges
edges = sharped.filter(ImageFilter.FIND_EDGES)
edges
- Enhancing Edges
en_edges = sharped.filter(ImageFilter.EDGE_ENHANCE)
en_edges
- Emboss Filter
emb = sharped.filter(ImageFilter.EMBOSS)
emb
This is just an introduction to the image processing capabilities of the Pillow. All these functions are helpful in the initial stage of image processing. There are many advanced functions that can be used at a later stage.
Conclusion:
In this article, we have seen the basic image processing capabilities of the Pillow. We saw how we can access different image attributes, how we can perform different operations like transpose, resize, etc. This is just an introduction to what all Pillow can do.