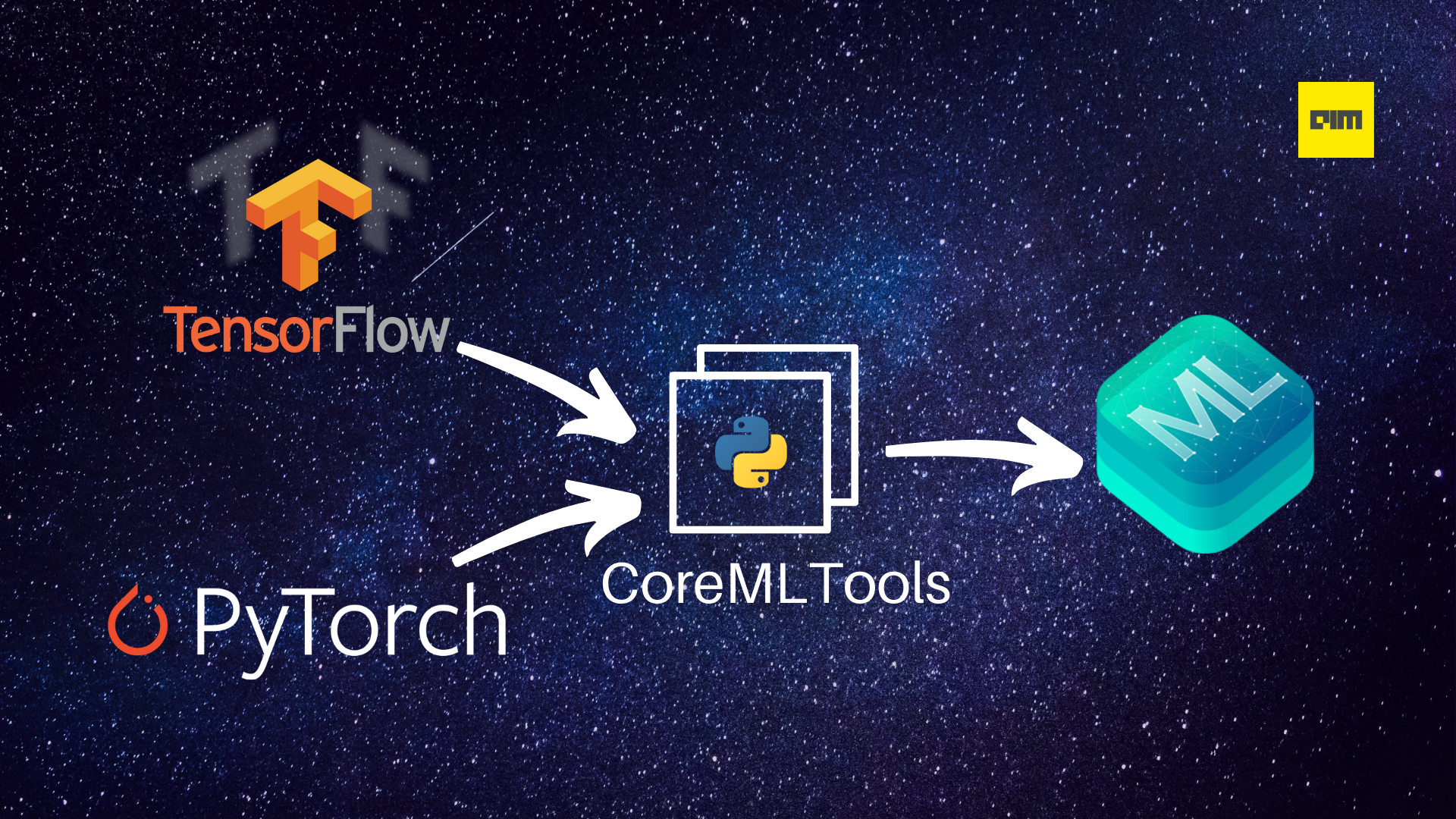
Core ML is an Apple framework that allows developers to integrate machine learning/deep learning models into their applications. However, it does not support model creation and training, i.e., you first need to create the model in a framework like TensorFlow or PyTorch, then you can convert and use it. There are two ways you can convert your machine learning model from the framework of your choice to the Core ML model format: through an intermediary model format like ONNX or by using Apple’s own CoreMLTools Python library.
Although ONNX works just fine for the conversion, CoreMLTools offers other useful functionalities like model optimization. Also, you’ll need to use CoreMLTools for the final conversion from ONNX format to Core ML format anyway. Currently, it supports the conversion of models created using the following libraries:
- PyTorch
- TensorFlow 1.x & 2.x
- TensorFlow’s Keras APIs
- scikit-learn
- XGBoost
- LibSVM
Installation
Install CoreMLTools from PyPI.
The package is only available for macOS (10.13+) and Linux.
pip install coremltools
You can learn more about the other methods of the installation here.
Converting models into Core ML model using CoreMLTools
From PyTorch
For conversion from PyTorch, you can either use the TorchScript object or TorchScript object saved as a .pt file.
- Create and train or load a pre-trained model and set it to evaluation mode.
import torch import torchvision import coremltools as ct # load a pre-trained MobileNetV2 model torch_model = torchvision.models.mobilenet_v2(pretrained=True) # set it to evaluation mode torch_model.eval()
- Create TorchScript object using the
torch.jit.traceand random data
random_input = torch.rand(1, 3, 224, 224) traced_model = torch.jit.trace(torch_model, random_input)
- Convert the TorchScript object to Core ML using the CoreMLTools
convert()method and save it.
# Convert to Core ML using the Unified Conversion API model = ct.convert( traced_model, inputs=[ct.ImageType(name="input_1", shape=random_input.shape)] )
- Make predictions on the converted model using the
predict()method.
Note: This is only supported on macOS version 10.13 or later.
from PIL import Image
example_image = Image.open("test.jpg").resize((224, 224))
out_dict = model.predict({"input_1": example_image})
From TensorFlow
For conversion from TensorFlow 2.x you can use tf.keras.Model object, HDF5 .H5 file, SavedModel path or concrete functions. For TensorFlow 1.x, CoreMLTools also supports frozen grpah (tf.Graph) objects and .pb file path.
- Create and train or load a pre-trained model and set it to evaluation mode.
import tensorflow as tf import coremltools as ct model = tf.keras.Sequential( [ tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)), tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu), tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation=tf.nn.softmax), ] ) # get the data (X_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data() model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy']) # fit the model model.fit(X_train, y_train, batch_size=32)
- Convert the TensorFlow model object using the convert() method.
mlmodel = ct.convert(model)
- Make a prediction using the predict() method.
Note: This is only supported on macOS version 10.13 or later.
import numpy as np
from IPython.display import display
from PIL import Image
img = Image.open('two.png').resize((28, 28)).convert('L')
display(img)
output = mlmodel.predict({"input_1": example_img})
print(output)
Colab Notebook of the above implementation.
References
For a more comprehensive understanding of CoreMLTools, refer to the following resources: