Google recently unveiled a new model that automatically generates formulas based on the rich context around a target cell. For example, when a user starts writing a formula with the ‘=’ sign in a target cell, the system generates possible relevant formulas for that cell by learning patterns of formulas in historical spreadsheets.
The way it works is that the model uses the data present in neighbouring rows and columns of the target cell and the header row as context. It does this by first embedding the contextual structure of a spreadsheet table, consisting of neighbouring and header cells, and then generating as two components:
- The sequence of operators (SUM, IF, etc.)
- The corresponding ranges on which the operators are applied (“A2:A10”)
The feature based on this model is generally available to Google Sheets users.
Previously, Google had developed tools to understand patterns in spreadsheet data to fill missing values in a column automatically; however, they were not built to support the process of writing formulas. Surprisingly, the latest development comes to light nearly after six years. In 2006, Google acquired XL2Web and turned it into Google Labs Spreadsheets.
Today, hundreds of millions of people apply formulas in those spreadsheets, allowing users to perform complex analyses and transformations on their data. Even though formula languages are simpler than general-purpose programming languages, writing these formulas can still be cumbersome and tedious.
Introducing SpreadsheetCoder
In a research paper, ‘SpreadsheetCoder: Formula Prediction from Semi-structured Context,’ published at ICML 2021, Google researchers proposed SpreadsheetCoder, a BERT-based model architecture to represent the tabular context in both row and column-based formats.
The model uses an encoder-decoder architecture that allows the flexibility to embed multiple types of contextual information in the encoder, which the decoder can use to generate desired formulas. Here’s an overall architecture of the formula prediction model:
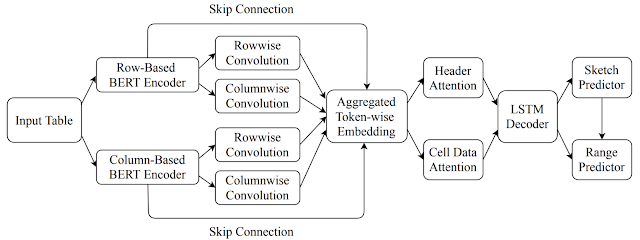
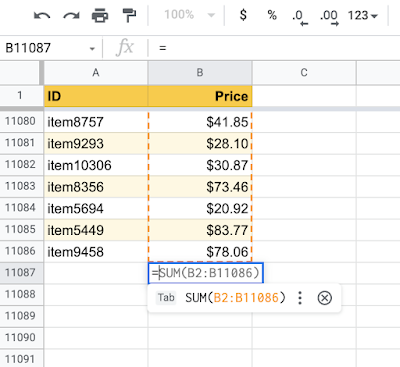
Besides this, the model also uses additional information from the high-level sheet structure, such as headers. Using Google Cloud TPUs for model predictions, the researchers ensured low latency on generating formula suggestions and could handle more requests on fewer machines. For example, the model can learn ranges that span thousands of rows (as shown below).
Outcome
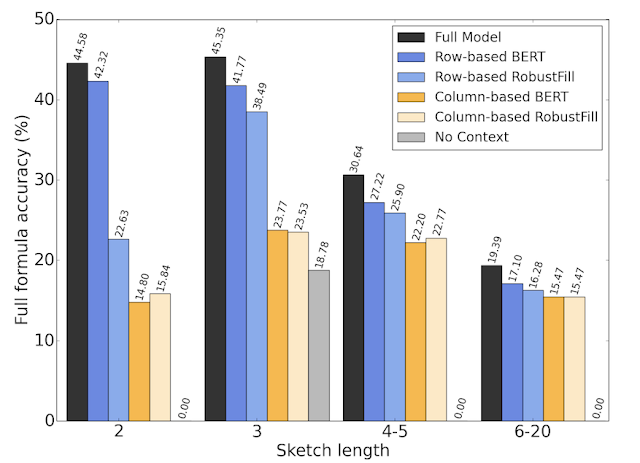
Google researchers said that they trained the model on a large dataset of spreadsheets and showed that SpreadsheetCoder achieves a top-1 prediction accuracy of 42.5 per cent, which is a considerable improvement over baselines that do not employ rich tabular context. Also, compared to the rule-based system, the latest model assists 82 per cent more users in composing formulas on Google Sheets.
On further study, the researchers noted that removing different components found that having row- and column-based context embedding and header information is important for models to perform well.
What’s new?
In this model, Google presented the first technique to synthesize spreadsheet formulas given a tabular context, including both cell values and headers – where they developed SpeadsheetCoder, to facilitate formula predictions.
In the coming years, Google researchers said that there are several exciting research directions, designing new model architectures to incorporate more tabular structure and extending the model to support more applications such as bug detection and automated chart creation in spreadsheets.